The standardization of excipients involves evaluating the excipient’s chemical and physical properties, impurity profile, and functionality.
It involves all means of obtaining and guaranteeing appropriate excipient performance standards to be explored.
INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION
Excipient quality plays a vital role in assuring safety, quality and efficacy of dosage forms. Standardization of excipient usually assures the customers and manufacturers that the excipient quality will meet the international market.
The various reasons for which excipients must be standardized are:
- To assure the customer that the excipients used are safe and will not alter the formulation and cause undesirable effects.
- To assure the manufacture that he is using a standard quality material for formulating his dosage form
- To reduce resources to host frequent customer audits and assure excipient GMP audit is conducted against appropriate GMP conformance expectations.
The standard chosen as framework for quality management system is ISO 9001. The Iso certification has the advantage of assuring the customers that excipient manufacturer’s quality management system has been verified independently.
GMP practice for excipients assures product integrity, avoid product contamination etc.
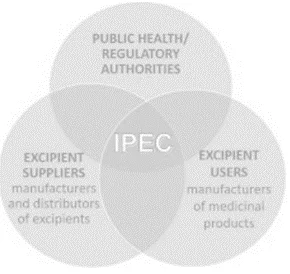
IPEC is an international industry association which is formed with the main objective of development and harmonization of international excipient standard and development of newer excipients. It deals with three kinds of stakeholder groups viz; suppliers, users and regulatory authorities. It is necessary to obtain sufficient data about the excipient and the manufacturer or distributer, usually to get such information and information of the excipient in detail the users and customers send questionnaires to the supplier, the questionnaire consists of large amount of queries which becomes very difficult to resolve and address every individual as lot of time and money is wasted during this process, hence in order to minimize this stressful process.
Standardized excipient package
IPEC has put forward an standardized excipient package that comprises of
- Product regulatory database
- Site quality overview
- Site and supply chain security overview.
Product regulatory database: – this document has been formed with the main objective of providing information about important physical properties, manufacturing and regulatory information specific to excipients to the user which facilitates the use of excipients in drug formulations. The various sections included are
- General product information: this includes information like product identification , product code/name, scope of document, and any other information that is necessary,
- Manufacturing, packaging, release and supplier information: describes the this information section regarding excipient manufacturing site and the information related with it, for e.g.:- manufacturing processing, packaging, product release warehousing, laboratory site etc, distribution channels, GMP or GDP compliance statements, information etc. equipment
- Physicochemical information: this section deals with the information related to the physical and chemical characteristics of the product for e.g. CAS number, information about the origin of excipients, their synonyms, its morphological characteristics, processes applied during manufacturing, mixed excipient information and the country of its origin if applicable.
- Regulatory information: this section describes the regulatory status of an excipient, it includes information like compendia compliance (e.g. USP-NF, Food chemicals codex, BP etc) drug master file, or European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines and healthcare (EDQM) certificate of suitability, viral safety, allergens, hypersensitivity information, residual solvent information, metal catalyst and metal reagent residue information. Kosher/Halal status, bioburden/ pyrogen (optional) information etc.
- Miscellaneous product information: this section includes information like lot/batch number, expiry date, use, nutritional information (if information etc.
- Revision: this section provides information regarding version control for document.
- Contact information: this section includes the contact details of the supplier.
Site quality overview: this document gives information regarding the site of manufacturing, and any other areas related to the excipient processing or testing, there are various sections that are included in this document which are as follows:
- Site overview: it describes supplier’s organization and production capabilities, topics included in this section are site name, address, corporate ownership, customers audit policy (optional) site details etc.
- Compliance evidence: this section describes information of facilities being provided e.g. ISO certification, GMP inspection by competent authority, GMP statements, external audit programs like International Pharmaceutical Excipients Auditing (IPEA), AIB international, GMASAFE, etc.
- IPEC-PQG GMP compliance: this section deals with information about how the suppliers comply with the applicable elements of IPEC-PQG-GMP guide.
- Miscellaneous site information: this includes any additional information provided (optional).
- Other information includes the contact details etc.
Site and supply chain security overview: This document deals with information regarding protection of product and continuity of supply as assured by supplier, this document includes information about site name, address, evaluation of carrier, tamper evident packaging, qualification of distributer, broker, intermediate storage location, repackaging, relabeling activities, FDA registration information , security, safety and environmental considerations etc. Thus these documents help in assuring the user, customer and supplier about the quality of excipient and may also give assurance that this process will continue to provide excipients of good and standard quality.
Excipient stability testing
Excipient stability testing
The stability studies are designed on the basis of following factors like
1) utilization of historical data about a particular excipient and drawing conclusions about excipient stability.
2) Conducting stability studies using excipients packed in commercial packaging placed in different warehouses where the temperature is monitored.
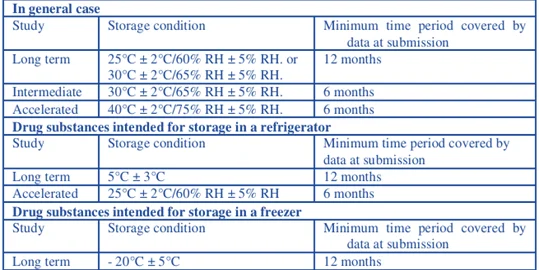
3) Conducting studies using conditions and recommendations as in ICHQ 1A (R2):- These guidelines serve the purpose of stability testing which provides the evidence of the quality of drug products under influence of various climatic conditions. Choice of test conditions are based on the analytic effects of climatic conditions in three regions namely Europe, Japan and United states.
Following procedures are followed in accordance to the guidelines:
1) Stress testing: it helps to identify the degradation products within the formulations. Such testing’s are carried in single batch where the effect of temperature is tested where the temperature is kept in increments of 100c for e.g. 500c, 600c etc above which accelerated stability testing is performed. Humidity is maintained at around 75% RH or greater for the testing procedure. Photo stability testing forms an integral part of stress testing where the excipients are exposed to conditions as mentioned in ICHQ 1B.
2) Specifications: specifications to analytical procedures are followed as per the guidelines mentioned in ICHQ 6A and ICHQ 6B, and for degradation products as in ICHQ 3A.
3) Testing frequency: for long term storage conditions testing is carried out every three months over first year, every six months over second year, and annually thereafter. For accelerated stability studies testing carried out at 0 month, 3 month, and 6 month. Testing over period of 6 months is generally recommended.
1) Storage conditions: excipients are tested for the storage conditions for its thermal stability, moisture sensitivity or solvent loss.
Stability indicating test methods: – Excipients should be tested for their stability using stability indicating assay methods, microbiological, physical and chemical tests, Chemical stability can be measured by chromatographic techniques, physical stability by microscopy, particle size analysis, in vitro dissolution tests etc. Various analytical tools such as thermal analysis, chromatographic techniques, diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, etc are used in detection and characterization of the excipient compatibility. Stability considerations should also be given to comparison of composition profile of excipient at the limit of its retest/ revaluation intervals if appropriate to that of excipients at time zero, the composition should remain unchanged within the recommended storage conditions.