ICH Guidelines are a global standard for developing and registering pharmaceuticals and medical products. They bring together regulatory authorities from different regions, including the United States, Europe, Japan, and others, to establish uniform requirements.
Introduction
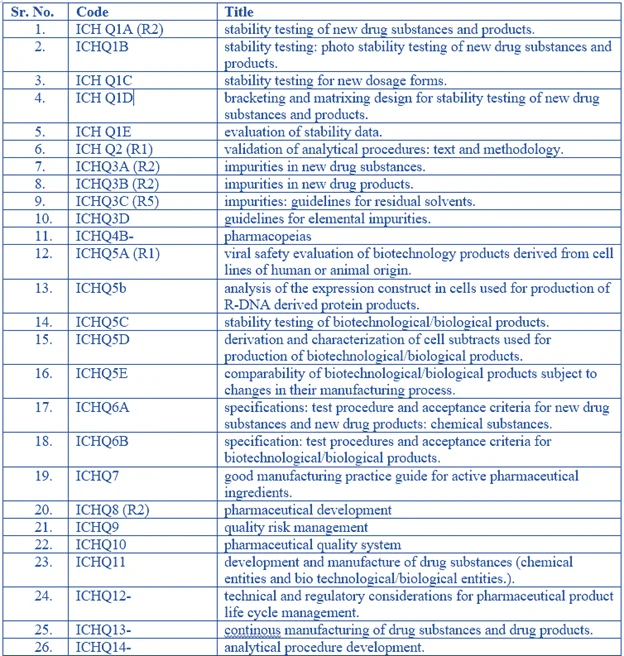
ICH guidelines – “Q” series (quality guidelines) – A review
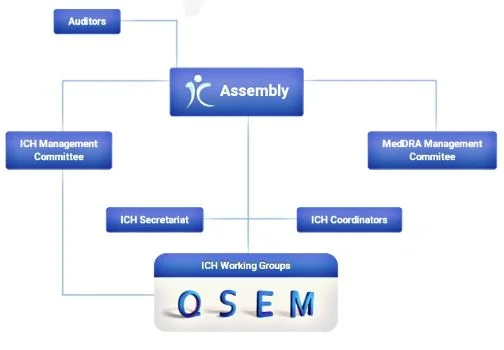
International council for harmonization of technical requirements for pharmaceuticals for human use is unique in bringing together the regulatory authorities and pharmaceutical industry to discuss scientific and technical aspects of drug registration. It’s mission is to achieve greater harmonization worldwide to ensure that safe, effective and high quality medicines are developed and registered in the most resource –efficient manner. Harmonization achievements in quality area include pivotal milestone such as the conduct of stability studies, defining relevant thresholds for impurities testing and a more manufacturing practice (GMP) risk management.
All Codes
ICH process
The ICH process
There are five stages in this process for developing a new guideline (denoted a “major topic”). The process starts with consideration of the new topic and development of a consensus by the relevant Expert Working Group (EWG). The EWG members are nominated from the regulatory and industrial bodies in the three regions. The draft consensus resulting from the EWG is then released by the ICH Steering Committee for wider consultation in the three sponsoring regions.
The Common Technical Document
ICH Topic M4 has been the most ambitious undertaking, aiming as it has to provide the basis for a single set of registration documents to support an application for marketing authorisation in any of the three ICH regions. It is closely linked to Topic M2 on electronic submission of documents which has set out standards to allow data interchange between industry and regulatory agencies. There are differences in regulatory practice in the three regions; in particular in the way authorities
Quality guidelines
There are eight quality topics under the auspices of ICH, including one in the planning stages, each with one or more associated guidelines. Some of these are described in more detail below where they are of relevance to the use of quantitative NMR in the drug registration process. The technical guidelines discussed relate to specifications and tests (Q6), impurities (Q3), validation of analytical methods (Q2) and stability (Q1).
Specifications and tests
Specifications, comprising sets of test procedures and acceptance criteria, are the fundamental basis for the control of the quality of either a drug substance or a medicinal product both at release and during its shelf life. ICH Topic Q6A Specifications: Test Procedures and Acceptance Criteria for new drug substances and new drug products: Chemical Substances reached Step 4 in October 1999 and was approved by the CPMP in November 1999 (CPMP/ICH/367/96) with a date of May 2000 (Step 5).
Chiral drug substances
That chiral substances may need specific identification testing or performance of a chiral assay for successful identification is acknowledged by the guideline. It is worth considering chiral substances in more detail as NMR has been such a successful tool for characterising these compounds. Tests for chiral drug substances are included in the category of specific tests/criteria.
Control of impurities
Two guidelines on impurities are discussed here: Topics Q3A makes recommendations on Impurities in new drug substances and Topic Q3B on Impurities in new medicinal products. In Europe, the guidelines were approved, respectively, as CPMP/ICH/142/95 and its Annex CPMP/ICH/282/95 in May 1995. Revisions to these the drug substance guideline was made in February 2002 and mainly affected the expression of threshold levels and harmonisation with Q3B.
Analytical validation
There are two ICH guidelines on analytical validation. The first provides a glossary of terms and the second addresses methodology. The first guideline, ICH Topic Q2A Validation of analytical procedures: Definitions and terminology, reached Step 4 in October 1994. It sought only to present a collection of terms and definitions and not to provide direction on how to accomplish validation.
Stability
Stability studies are used to establish the re-test period for the active ingredient – that is the length of time it can be stored and used without analysing immediately before use – and the shelf life of the finished product. The release and shelf life specifications for the product may differ to accommodate degradation of the active ingredient or other acceptable changes which may occur on storage.
Pharmacopoeial harmonisation
Pharmacopoeial harmonisation under the auspices of the Pharmacopoeial Discussion Group (PDG) started before ICH and the two bodies have maintained close links. Stimulated by the publication of Topic Q6 on specifications and tests, ICH Topic Q4B, Regulatory acceptance of pharmacopoeial interchangeability was established in November 2003 with the aim of facilitating regulatory implementation of harmonised pharmacopoeial monographs.
Concluding remarks
Concluding remarks
The success of ICH has been based on the achievement of scientific consensus and the commitment of the three participating regulatory authorities to implement harmonised guidelines. Having succeeded in harmonising the format of the registration dossier and its electronic counterpart, ICH has declared a focussed programme of implementation and maintenance to ensure that the process keeps pace with the changing international environment.

