The action or process of disinfecting or purifying an area with the fumes of certain chemicals is fumigation method in medical and non-medical fields.
Introduction of fumigation method in medical and non-medical fields
In the twentieth century, fumigation became a very popular method of disinfection, although in the same century many agents used as fumigants were withdrawn for ecological reasons. Fogging (fumigation) is a relatively new disinfection technology using dry fog, which behaves more like a gas and easily fills the sanitized space, reaching all surfaces in the room. The undoubted advantage of fumigation is the possibility of disinfecting difficult to clean areas. Fumigation has become particularly important in the twenty-first century due to procedures related to combating and preventing the spread of the coronavirus that causes COVID-19. Objective.
The aim of this review article is to summarize the current state of knowledge in the field of disinfection by air, based on the results of original scientific research, and to identify new trends in its application.
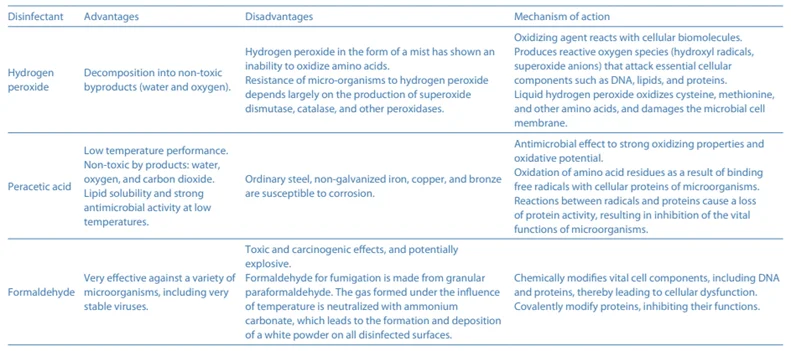
Brief description of the state of knowledge. Due to the fact that fumigation is safe for apparatus, equipment, and electronics, while simultaneously enabling the highest possible bactericidal and virucidal levels, this method is widely used in various areas, both medical and non-medical. Fogging technology is used in the medical, pharmaceutical, and food industries, as well as in transportation, for air fumigation or surface disinfection in closed spaces, such as hospital and laboratory rooms, incubators, refrigerators, ships, trucks, railway containers, and aircraft, to name only a few. The most common fumigants are hydrogen peroxide and peracetic acid, and their mechanism of action is related to their oxidizing properties.
Methods of disinfecting the environment.
Disinfection of the environment is performed by direct or indirect methods using various products and processes.
- Direct methods are carried out using a liquid disinfectant that is spread over the surface to be disinfected.
- Indirect methods include fumigation, defined as an antimicrobial process performed indirectly in a closed space. An example of fumigation is fogging, the indirect application of a biocidal liquid in the form of a dry fog. A variety of oxidants is often used in the fumigation process, such as ozone, chlorine dioxide, and hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide is a widely used disinfectant and exhibits particularly rapid antimicrobial activity in gaseous form.
- The dry mist fogging technique ensures that the disinfectant does not condense and keeps the gas phase below the dew point,
- while the wet mist fogging process wets the surfaces being disinfected. The two processes differ in antimicrobial activity, compatibility with surfaces, and safety
Anti-microbial properties of fumigation agents:
- OBJECTIVE
To lay down the procedure of of the fumigation method in medical and non-medical fields
- SCOPE
This SOP shall be applicable for all the area of Production.
- RESPONSIBILITY
3.1 Execution: Operator
3.2 Checking: Production Pharmacist & Above
- ACCOUNTABILITY
HOD-Production / Assigned Designee
- PROCEDURE
5.1 Fumigation should be carried out at the end of the production operation twice in a month and whenever required.
5.2 Production person shall ensure that raw Material, finished goods, intermediates or in process goods should not be present in the area of Fumigation. If present cover all the materials with polythene bags.
5.3 Always use nose-mask and Goggles while doing fumigation is irritating to the human eye.
5.4 Windows, doors should be closed; AHU’s should be switched off before starting fumigation.
5.5 Place fumigating agent in the fogger and switch “ON” the fogger.
5.6 After fumigation of the area is complete, Switch “OFF” the fogger and affixed the label as “Area under fumigation, do not enter” on every side of the entrance. Allow the fumigation fumes to stay for about 6-7 hrs.
5.7 After the specified time of fumigation is over, enter the area only by starting exhaust for about 30 minutes.
5.8 Conduct cleaning before processing any product in the concerned area.
5.9 After 30 minutes, start the AHU’s allow to stabilize to attend required temperature and humidity then start the routine production operation.
5.10 Fill the “Fumigation Record”
Conclusion:
The ability to safely and reproducibly decontaminate enclosed areas like isolators and rooms is an important consideration to many industrial, research, and healthcare facilities. Traditionally, formaldehyde has been used, but safety and efficacy concerns have highlighted the need for alternative methods. Vaporized Hydrogen Peroxide, as used in STERIS Corporation’s VHP® Technology, is a dry gaseous method that has been used as a reliable alternative for aseptic processing isolators and more recently for room/facility decontamination.
Hydrogen peroxide and peracetic acid are highly effective and non-toxic fumigants that can be safely used for fogging laboratory and medical equipment, pharmaceutical facilities, hospital rooms, and animal breeding rooms.
Current Good Manufacturing Practice cGMP and the Concepts of Modern Quality Systems

